28|I/O多路复用进阶:子线程使用poll处理连接I/O事件
文章目录
你好,我是盛延敏,这里是网络编程实战第 28 讲,欢迎回来。
在前面的第 27 讲中,我们引入了 reactor 反应堆模式,并且让 reactor 反应堆同时分发 Acceptor 上的连接建立事件和已建立连接的 I/O 事件。
我们仔细想想这种模式,在发起连接请求的客户端非常多的情况下,有一个地方是有问题的,那就是单 reactor 线程既分发连接建立,又分发已建立连接的 I/O,有点忙不过来,在实战中的表现可能就是客户端连接成功率偏低。
再者,新的硬件技术不断发展,多核多路 CPU 已经得到极大的应用,单 reactor 反应堆模式看着大把的 CPU 资源却不用,有点可惜。
这一讲我们就将 acceptor 上的连接建立事件和已建立连接的 I/O 事件分离,形成所谓的主 - 从 reactor 模式。
主 - 从 reactor 模式
文章下面的这张图描述了主 - 从 reactor 模式是如何工作的。
主 - 从这个模式的核心思想是,主反应堆线程只负责分发 Acceptor 连接建立,已连接套接字上的 I/O 事件交给 sub-reactor 负责分发。其中 sub-reactor 的数量,可以根据 CPU 的核数来灵活设置。
比如一个四核 CPU,我们可以设置 sub-reactor 为 4。相当于有 4 个身手不凡的反应堆线程同时在工作,这大大增强了 I/O 分发处理的效率。而且,同一个套接字事件分发只会出现在一个反应堆线程中,这会大大减少并发处理的锁开销。
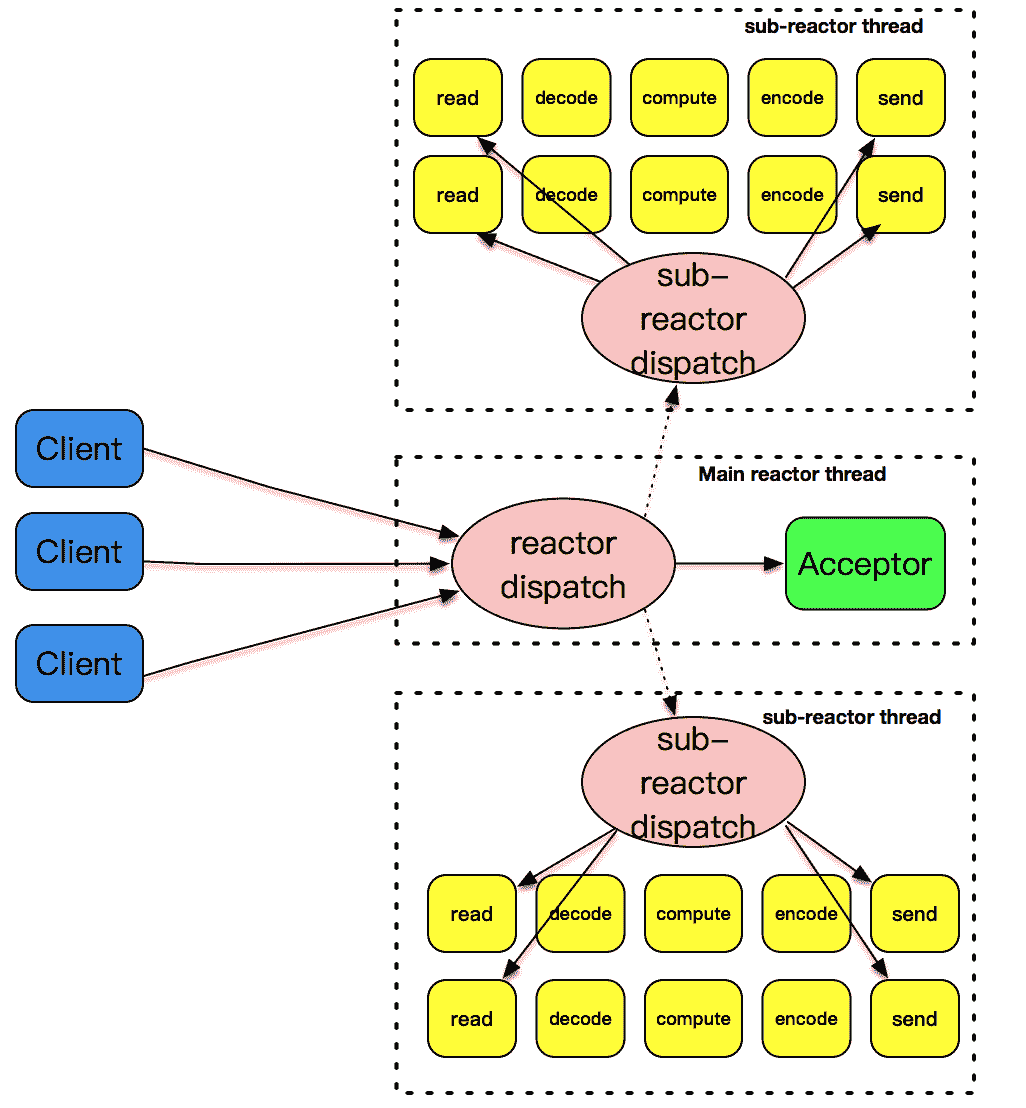
我来解释一下这张图,我们的主反应堆线程一直在感知连接建立的事件,如果有连接成功建立,主反应堆线程通过 accept 方法获取已连接套接字,接下来会按照一定的算法选取一个从反应堆线程,并把已连接套接字加入到选择好的从反应堆线程中。
主反应堆线程唯一的工作,就是调用 accept 获取已连接套接字,以及将已连接套接字加入到从反应堆线程中。不过,这里还有一个小问题,主反应堆线程和从反应堆线程,是两个不同的线程,如何把已连接套接字加入到另外一个线程中呢?更令人沮丧的是,此时从反应堆线程或许处于事件分发的无限循环之中,在这种情况下应该怎么办呢?
我在这里先卖个关子,这是高性能网络程序框架要解决的问题。在实战篇里,我将为这些问题一一解开答案。
主 - 从 reactor+worker threads 模式
如果说主 - 从 reactor 模式解决了 I/O 分发的高效率问题,那么 work threads 就解决了业务逻辑和 I/O 分发之间的耦合问题。把这两个策略组装在一起,就是实战中普遍采用的模式。大名鼎鼎的 Netty,就是把这种模式发挥到极致的一种实现。不过要注意 Netty 里面提到的 worker 线程,其实就是我们这里说的从 reactor 线程,并不是处理具体业务逻辑的 worker 线程。
下面贴的一段代码就是常见的 Netty 初始化代码,这里 Boss Group 就是 acceptor 主反应堆,workerGroup 就是从反应堆。而处理业务逻辑的线程,通常都是通过使用 Netty 的程序开发者进行设计和定制,一般来说,业务逻辑线程需要从 workerGroup 线程中分离,以便支持更高的并发度。
|
|
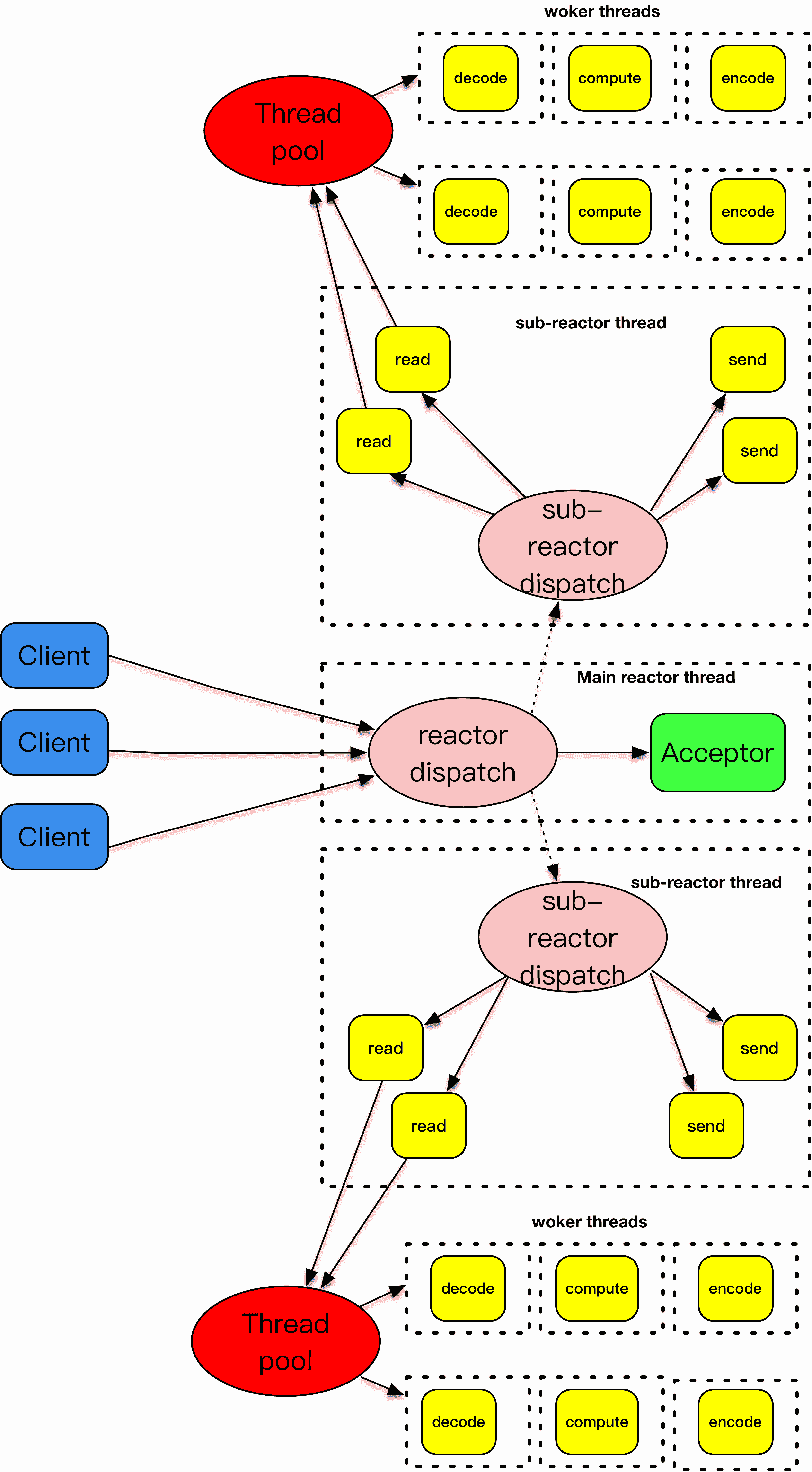
这张图解释了主 - 从反应堆下加上 worker 线程池的处理模式。
主 - 从反应堆跟上面介绍的做法是一样的。和上面不一样的是,这里将 decode、compute、encode 等 CPU 密集型的工作从 I/O 线程中拿走,这些工作交给 worker 线程池来处理,而且这些工作拆分成了一个个子任务进行。encode 之后完成的结果再由 sub-reactor 的 I/O 线程发送出去。
样例程序
|
|
我们的样例程序几乎和第 27 讲的一样,唯一的不同是在创建 TCPServer 时,线程的数量设置不再是 0,而是 4。这里线程是 4,说明是一个主 acceptor 线程,4 个从 reactor 线程,每一个线程都跟一个 event_loop 一一绑定。
你可能会问,这么简单就完成了主、从线程的配置?
答案是 YES。这其实是设计框架需要考虑的地方,一个框架不仅要考虑性能、扩展性,也需要考虑可用性。可用性部分就是程序开发者如何使用框架。如果我是一个开发者,我肯定关心框架的使用方式是不是足够方便,配置是不是足够灵活等。
像这里,可以根据需求灵活地配置主、从反应堆线程,就是一个易用性的体现。当然,因为时间有限,我没有考虑 woker 线程的部分,这部分其实应该是应用程序自己来设计考虑。网络编程框架通过回调函数暴露了交互的接口,这里应用程序开发者完全可以在 onMessage 方法里面获取一个子线程来处理 encode、compute 和 encode 的工作,像下面的示范代码一样。
|
|
样例程序结果
我们启动这个服务器端程序,你可以从服务器端的输出上看到使用了 poll 作为事件分发方式。
多打开几个 telnet 客户端交互,main-thread 只负责新的连接建立,每个客户端数据的收发由不同的子线程 Thread-1、Thread-2、Thread-3 和 Thread-4 来提供服务。
这里由于使用了子线程进行 I/O 处理,主线程可以专注于新连接处理,从而大大提高了客户端连接成功率。
|
|
总结
本讲主要讲述了主从 reactor 模式,主从 reactor 模式中,主 reactor 只负责连接建立的处理,而把已连接套接字的 I/O 事件分发交给从 reactor 线程处理,这大大提高了客户端连接的处理能力。从 Netty 的实现上来看,也遵循了这一原则。
思考题
和往常一样,给大家留两道思考题:
第一道,从日志输出中,你还可以看到 main-thread 首先加入了 fd 为 4 的套接字,这个是监听套接字,很好理解。可是这里的 main-thread 又加入了一个 fd 为 7 的套接字,这个套集字是干什么用的呢?
第二道,你可以试着修改一下服务器端的代码,把 decode-compute-encode 部分使用线程或者线程池来处理。
欢迎你在评论区写下你的思考,或者在 GitHub 上上传修改过的代码,我会和你一起交流,也欢迎把这篇文章分享给你的朋友或者同事,一起交流一下。

文章作者 anonymous
上次更新 2024-05-12